These are used to redefine or restrict the domain of tf objects.
Arguments
- f
a
tf-object- begin
numeric vector of length 1 or
length(f). Defaults to the lower limit of the domain off.- end
numeric vector of length 1 or
length(f). Defaults to the upper limit of the domain off.- ...
not used
Value
an object like f on a new domain (potentially).
Note that regular functional data and functions in basis representation will
be turned into irregular tfd-objects iff begin or end are not scalar.
Examples
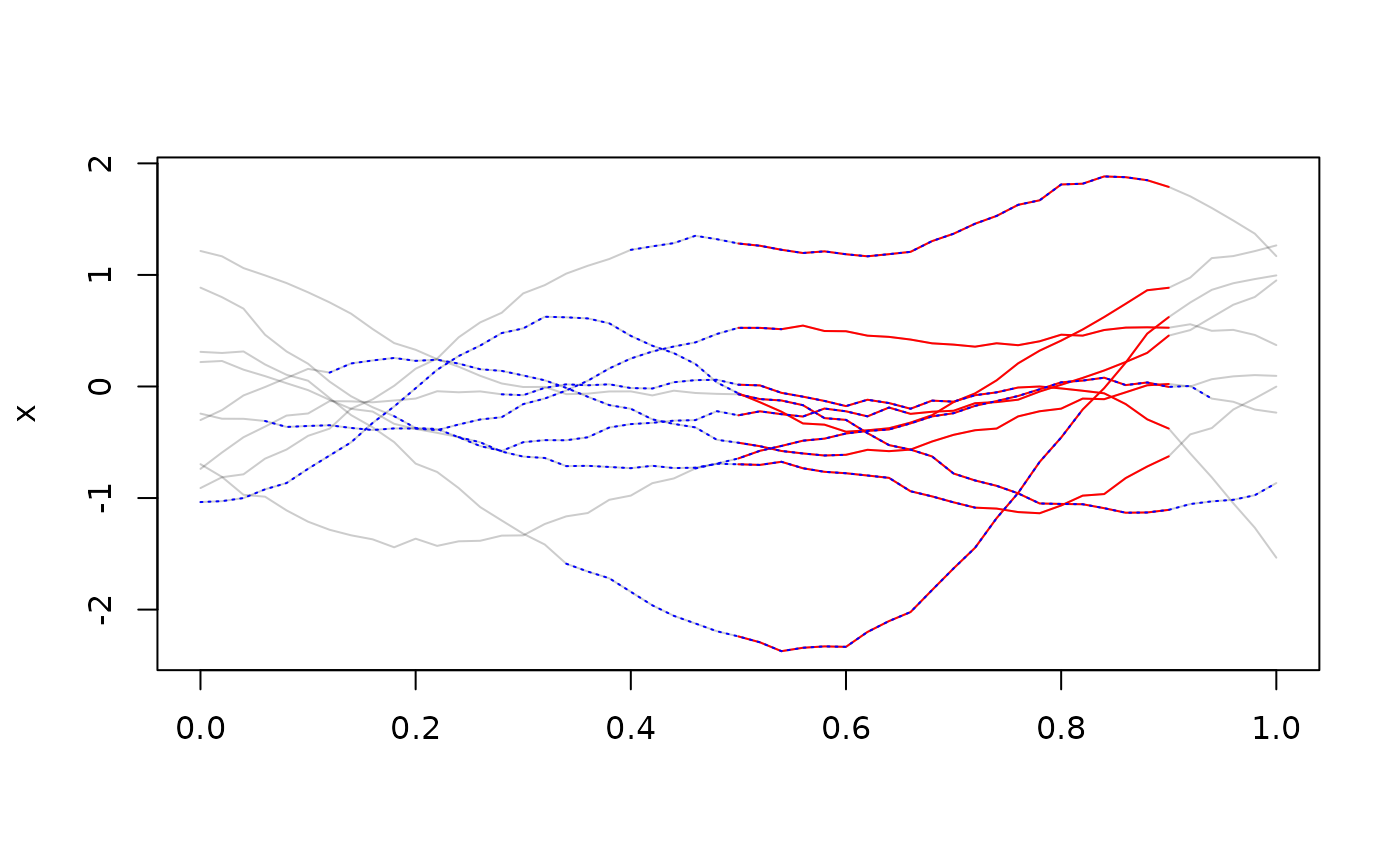
x <- tf_rgp(10)
plot(x)
tf_zoom(x, 0.5, 0.9)
#> tfd[10] on (0.5,0.9) based on 21 evaluations each
#> interpolation by tf_approx_linear
#> 1: (0.50,-0.062);(0.52,-0.141);(0.54,-0.226); ...
#> 2: (0.50, 0.53);(0.52, 0.53);(0.54, 0.51); ...
#> 3: (0.50, -0.50);(0.52, -0.54);(0.54, -0.58); ...
#> 4: (0.50, -0.26);(0.52, -0.22);(0.54, -0.25); ...
#> 5: (0.50, -0.70);(0.52, -0.70);(0.54, -0.67); ...
#> [....] (5 not shown)
tf_zoom(x, 0.5, 0.9) |> lines(col = "red")
tf_zoom(x, seq(0, 0.5, length.out = 10), seq(0.5, 1, length.out = 10)) |>
lines(col = "blue", lty = 3)